Here’s What American Express Company’s (NYSE:AXP) P/E Is Telling Us

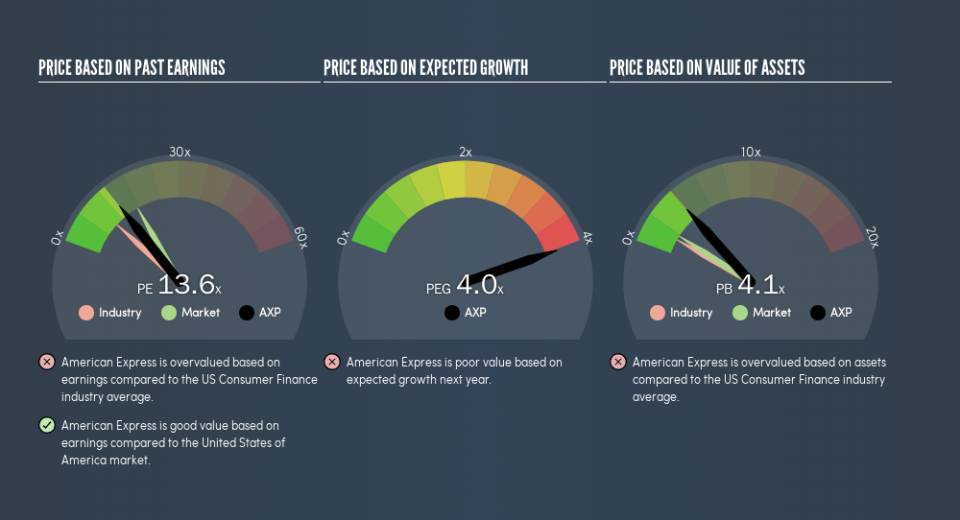
The goal of this article is to teach you how to use price to earnings ratios (P/E ratios). To keep it practical, we’ll show how American Express Company’s (NYSE:AXP) P/E ratio could help you assess the value on offer. American Express has a P/E ratio of 13.62, based on the last twelve months. That corresponds to an earnings yield of approximately 7.3%.
Check out our latest analysis for American Express
How Do I Calculate American Express’s Price To Earnings Ratio?
The formula for P/E is:
Price to Earnings Ratio = Share Price ÷ Earnings per Share (EPS)
Or for American Express:
P/E of 13.62 = $107.98 ÷ $7.93 (Based on the trailing twelve months to December 2018.)
Is A High Price-to-Earnings Ratio Good?
A higher P/E ratio means that investors are paying a higher price for each $1 of company earnings. All else being equal, it’s better to pay a low price — but as Warren Buffett said, ‘It’s far better to buy a wonderful company at a fair price than a fair company at a wonderful price.’
How Growth Rates Impact P/E Ratios
Companies that shrink earnings per share quickly will rapidly decrease the ‘E’ in the equation. That means even if the current P/E is low, it will increase over time if the share price stays flat. A higher P/E should indicate the stock is expensive relative to others — and that may encourage shareholders to sell.
Notably, American Express grew EPS by a whopping 165% in the last year. But earnings per share are down 2.3% per year over the last five years.
How Does American Express’s P/E Ratio Compare To Its Peers?
The P/E ratio essentially measures market expectations of a company. The image below shows that American Express has a higher P/E than the average (9.7) P/E for companies in the consumer finance industry.
American Express’s P/E tells us that market participants think the company will perform better than its industry peers, going forward. The market is optimistic about the future, but that doesn’t guarantee future growth. So further research is always essential. I often monitor director buying and selling.
Don’t Forget: The P/E Does Not Account For Debt or Bank Deposits
The ‘Price’ in P/E reflects the market capitalization of the company. That means it doesn’t take debt or cash into account. Hypothetically, a company could reduce its future P/E ratio by spending its cash (or taking on debt) to achieve higher earnings.
Spending on growth might be good or bad a few years later, but the point is that the P/E ratio does not account for the option (or lack thereof).
How Does American Express’s Debt Impact Its P/E Ratio?
Net debt totals 38% of American Express’s market cap. This is a reasonably significant level of debt — all else being equal you’d expect a much lower P/E than if it had net cash.
The Verdict On American Express’s P/E Ratio
American Express’s P/E is 13.6 which is below average (17.4) in the US market. The company hasn’t stretched its balance sheet, and earnings growth was good last year. The low P/E ratio suggests current market expectations are muted, implying these levels of growth will not continue.
Investors have an opportunity when market expectations about a stock are wrong. As value investor Benjamin Graham famously said, ‘In the short run, the market is a voting machine but in the long run, it is a weighing machine.’ So this free visualization of the analyst consensus on future earnings could help you make the right decision about whether to buy, sell, or hold.
But note: American Express may not be the best stock to buy. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies with strong recent earnings growth (and a P/E ratio below 20).
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.